- Text consists of characters (letters, numbers, punctuation marks, or any other symbol requiring one byte of computer storage space) that are used to create words, sentences, and paragraphs.
- Graphics are digital representations of nontext information such as drawings, charts, photographs, and animation (a series of still images in rapid sequence that gives the illusion of motion).
- Audio is music, speech, or any other sound.
- Video consists of images played back at speeds to provide the appearance of full motion.
- An output device is any computer component capable of conveying information to a user.
2. The characteristics of LCD monitors, LCD screens, plasma monitors, and HDTVs.
A liquid crystal display (LCD) is a thin, flat electronic visual display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals (LCs). LCs do not emit light directly.They are used in a wide range of applications, including computer monitors, television, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, signage, etc. They are common in consumer devices such as video players, gaming devices, clocks, watches, calculators, and telephones. LCDs have displaced cathode ray tube (CRT) displays in most applications. They are usually more compact, lightweight, portable, less expensive, more reliable, and easier on the eyes.They are available in a wider range of screen sizes than CRT and plasma displays, and since they do not use phosphors, they cannot suffer image burn-in.
LCDs are more energy efficient and offer safer disposal than CRTs. Its low electrical power consumption enables it to be used in battery-powered electronic equipment. It is an electronically modulated optical device made up of any number of pixels filled with liquid crystals and arrayed in front of a light source (backlight) or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. The earliest discovery leading to the development of LCD technology, the discovery of liquid crystals, dates from 1888. By 2008, worldwide sales of televisions with LCD screens had surpassed the sale of CRT units. Plasma display screens are made from glass, which reflects more light than the material used to make an LCD screen. This causes glare from reflected objects in the viewing area. Companies such as Panasonic coat their newer plasma screens with an anti-glare filter material. Currently, plasma panels cannot be economically manufactured in screen sizes smaller than 32 inches. Although a few companies have been able to make plasma EDTVs this small, even fewer have made 32in plasma HDTVs. With the trend toward larger and larger displays, the 32in screen size is rapidly disappearing. Though considered bulky and thick compared to their LCD counterparts, some sets such as Panasonic's Z1 and Samsung's B860 series are as slim as one inch thick making them comparable to LCDs in this respect. Competing display technologies include CRT, OLED, LCD, DLP, SED, LED, FED, and QLED. High-definition television (or HDTV) is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems (standard-definition TV, or SDTV, or SD). HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD. Early HDTV broadcasting used analog techniques, but today HDTV is digitally broadcast using video compression. Some personal video recorders (PVRs) with hard disk storage but without high-definition tuners are described as "HD", for "Hard Disk", which can be a cause of confusion.
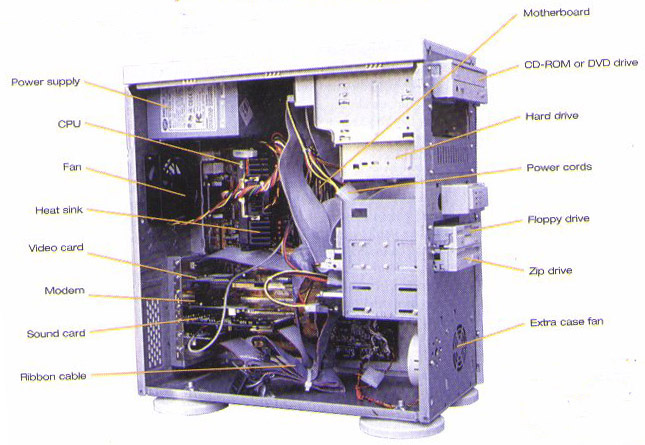
3. What are the components inside the systems units.
4. The components of a processor and how they complete a machine cycle.
- A machine cycle consists of a sequence of three steps that is performed continuously and at a rate of millions per second while a computer is in operation. They are fetch,decode and execute. There also is a fourth step, store, in which input and output from the other three phases is stored in memory for later use; however, no actual processing is performed during this step.
- The control unit is a part of the CPU that also decodes the instruction in the instruction register. A register is a very small amount of very fast memory that is built into the CPU in order to speed up its operations by providing quick access to commonly used values; instruction registers are registers that hold the instruction being executed by the CPU.
5. Define a bit and describe how a series of bits represents data.
· A bit (a contraction of binary digit) is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states. These may be the two stable states of a flip-flop, two positions of an electrical switch, two distinct voltage or current levels allowed by a circuit, two distinct levels of light intensity, two directions of magnetization or polarization, etc.
In computing, a bit can also be defined as a variable or computed quantity that can have only two possible values. These two values are often interpreted as binary digits and are usually denoted by the Arabic numerical digits 0 and 1. Indeed, the term "bit" is a contraction of binary digit. The two values can also be interpreted as logical values(true/false, yes/no), algebraic signs (+/−), activation states (on/off), or any other two-valued attribute. The correspondence between these values and the physical states of the underlying storage or device is a matter of convention, and different assignments may be used even within the same device or program. The length of a binary number may be referred to as its "bit-length."
6. Identify the categories of application software.
1. Personal productivity applications
2. Multimedia and Graphics applications
3. Communications applications
4. Home and educational
7. Identify the key features of widely used business programs.
8. What are the advantages of using application software on the Web.
9. History of the Internet.
10. What are diferent storage devices.